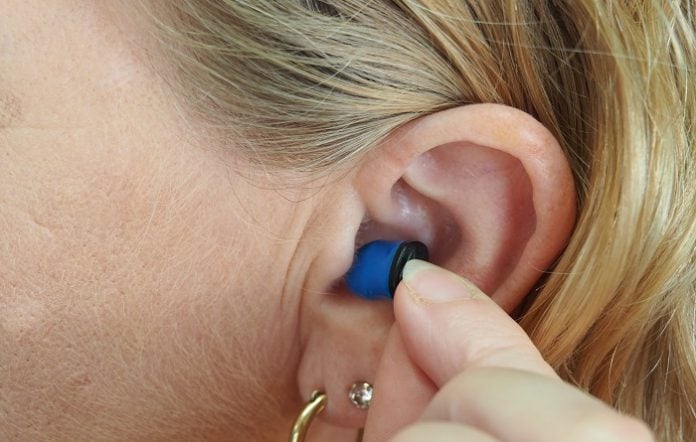
How to Choose The Best Hearing Aids for You
A hearing aid is an electronic device that fits in your ear and helps you hear better. It makes certain sounds louder to enable people with hearing loss or impairment to hear, communicate, and take part in everyday activities.
Knowing The Parts and Types of Hearing Aids
People with hearing problems often have difficulty hearing quiet sounds or hearing when there’s a lot of noise in the area. However, hearing aids can help them live comfortably by providing the best solution to their specific needs.
The basic components of hearing aids are a microphone, an amplifier, and a speaker. A microphone receives sound and converts it to electrical signals, while the amplifier sends them back to the hearing aid speaker so the person can hear properly.
Knowing the parts and types of hearing aids can help you select a product that’s best for you.
What can hearing aids do?
Hearing aids can be used to improve the hearing and comprehension of those who have hearing loss due to damage to the inner ear’s small sensory cells, also known as cochlear hair cells.
This is also known as sensorineural hearing impairment and this type of damage can be caused by disease, aging, injury from noise, and certain medications.
The hearing aid amplifies the sound vibrations entering the ear and converts them into neural signals which are then passed on to the brain by the remaining hair cells. The amplification is required to compensate for the hearing loss and it successfully enables people to enjoy sounds.
For example, if you have severe damage to the hair cells, you’ll need higher hearing aid amplification. However, there are limits on the amount of hearing aid amplification that can be safely provided.
Different types of hearing aids
There are different hearing aid styles and choosing one depends on a combination of both your individual hearing loss and your cosmetic preferences. There are a few types of hearing aids including behind-the-ear, in-the-ear, and in-canal hearing aid.
Behind-the-ear hearing aids (BTE) consist of a hard-plastic case that is worn behind the ear and connected to an earmold that fits in the outer ear. The case is where the electronic parts are kept, and the hearing aid transmits sound through the earmold into the ear. BTE aids can be used by anyone with mild to severe hearing loss.
In-the-ear (ITE) hearing aids, on the other hand, are designed to fit inside the ear. Generally, doctors recommend this type of hearing aid for patients with moderate to severe hearing loss. The hard plastic case holds the electronic components of the hearing aid and protects them from dirt and ear wax.
Furthermore, these hearing aids have telecoils, which are small magnetic coils that allow users to hear sound through the circuitry of their hearing aid rather than through its microphone. This allows patients with hearing loss to hear telephone conversations more clearly.
In-the-canal (ITC) hearing aids are made to fit within the ear canal and be completely concealed. This type of hearing aid is suitable for patients with mild to moderate hearing loss. It has features that don’t completely fit in the ITC hearing aids and can be difficult to adjust due to their small size. Also, they’re susceptible to earwax clogging the speaker of the hearing device.
Analog and Digital Hearing Aids
Analog hearing aids convert sound waves to electrical signals that are amplified. Each user will have their own hearing aid setting recommended by their audiologist since an analog or programmable hearing aid can have multiple settings or programs.
Usually, audiologists use a computer to program the hearing aids, and the program can be changed to suit different listening environments from a quiet, private room to a noisy restaurant and large open spaces, like a stadium or theater.
On the other hand, digital hearing aids convert sound waves to numerical codes and amplify them. The code can also include information about the sound’s pitch and loudness so that the hearing aid can be programmed to amplify certain frequencies more than others.
The digital circuitry allows an audiologist to adjust the hearing device to suit the user’s requirements, and can also be programmed to concentrate on specific sounds.
Wrap-Up
To find the right hearing aid for your needs you will have to learn about the parts and the way they work. But with the help of a professional, you will eventually find the right style and type of hearing aid that will enable you to enjoy sounds just like anyone else.
Before you decide to purchase a hearing device make sure you consult with an audiologist to recommend the best option for your specific needs.
Photo by Mark Paton on Unsplash