Is Proper Diet and Exercise Important when Treating Depression?
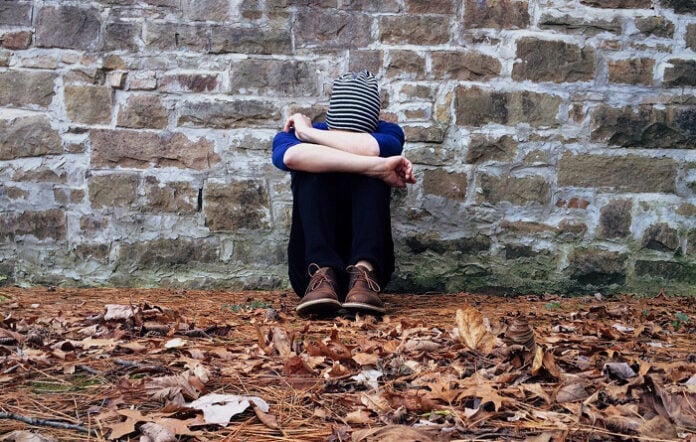
Mental illness poses a tremendous challenge to public health and wellness. The most severe mental diseases include anxiety-related disorders and depression.
A Multidimensional Understanding of Depression
Extensive research has been conducted on diet and depression, with astonishing available findings. Nowadays, a cornucopia of treatment options is available for depression, including:
● Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – this form of psychotherapy modifies thought patterns to shape thoughts and beliefs. Therapists use CBT for treating mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, OCD, PTSD, phobias, chronic pain, bipolar disorder, etc.
This short-term approach to therapy typically encompasses 20 sessions, but treatment can continue for longer if necessary. CBT is used to uncover unhealthy thought patterns affecting beliefs, mood, and perspective.
● SSRIs and SNRIs for treating depression and anxiety disorders – these medications include Zoloft, Paxil, Pexeva, Prozac, Celexa, and Lexapro. They are used for treating depression, sadness, and irritability. SNRIs have an impact on the neurotransmitters between brain cells via brain chemistry.
However, SNRIs can have many undesirable side effects: excessive sweating, headaches, dizziness, nausea, dry mouth, and sexual dysfunction.
● Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) – An increasingly popular treatment regimen is magnetic therapy for depression. Deep TMS™ is a proprietary technology that uses noninvasive methods to help ease symptoms related to mental health conditions.
Presently, BrainsWay Deep TMS is FDA-cleared to treat Major Depressive Disorder, Anxious Depression, OCD, and Smoking Addiction, in the United States and is CE Marked for various psychiatric and neurological conditions across Europe. Deep TMS utilizes a magnetic field courtesy of a patented H-Coil.
This is housed within a specially fitted helmet for a patient’s head. This form of depression therapy transmits magnetic pulses that penetrate deeper than traditional TMS into problematic areas. Deep TMS can elicit positive results by way of its effect on neural activity.
How Diet Affects Symptoms of Depression
Scientific studies confirm that individuals who adhere to medically-recommended diets tend to fare better vis-a-vis depressive symptoms than those who don’t.
This is because these approved diets expressly exclude processed foods. In addition, recommended diets are rich in folic acid, magnesium, Omega-3 fatty acids, fish, and foods with anti-inflammatory effects on the body.
A study conducted by Berk et al. found that managing depression was best achieved by lifestyle modifications. Factors that can increase the incidence of depression include smoking and drinking, inactivity, and poor diet. Since the Berk studies, additional studies have been conducted on depression vis-a-vis diet and nutrition.
Over the years, various studies on diet and depression have been authored by experts, and dramatic findings have been published:
● 2019 France; Adijibade et al. studied the relationship between depressive symptoms and an inflammatory diet. Findings suggest that pro-inflammatory diets may be correlated with an increased risk of depressive symptoms, particularly in obese individuals.
Additionally, a positive correlation exists between the consumption of processed foods and the incidence of depression. Therefore, mental health and wellness are best served by avoiding processed foods.
The studies evaluated the incidence of depression in patients who adhered to dietary advice from medical professionals. As expected, compliance with medical recommendations was associated with lower levels of depression.
Scientific studies suggest that the inflammatory effects of diet are associated with a higher incidence of depressive symptoms, particularly in at-risk groups such as smokers, physically inactive individuals, and various subgroups of males.
● 2017, USA; Bergmans and Malecki investigated the inflammatory index of diet and its association with mental health disorders, including depression. The findings indicate a higher risk of depression and chronic anxiety with a higher intake of inflammatory foods.
● 2019, the Netherlands; Elstgeest et al. investigated the relationship between diet quality and depression. The study suggests that depressive symptoms (current and past) are associated with a poor quality diet based on the dietary index of men.
The Impact of Fitness on Depressive Symptoms
Depressed individuals tend to avoid physical activity, despite the positive impact of an active lifestyle. However, experts worldwide agree that exercise can dramatically affect depression, alleviating the symptoms and improving the patient’s overall well-being.
In addition, exercise is beneficial for treating arthritis, diabetes, high blood pressure, anxiety, and depression. While the correlation between activity and depression is not ironclad, regular exercise has positive effects.
Physical activity has the dual benefit of distracting individuals from whatever worries them. While working out, the mind re-focuses attention away from problems. This breaks the pattern of negative thoughts and anxiety-riddled behavior. More importantly, exercise releases endogenous cannabinoids, a.k.a. endorphins which help to enhance our sense of well-being.
There are many other positive health and wellness effects of regular exercise, notably increased social behavior among people, increased self-confidence by feeling better emotionally, physically, and spiritually, and focusing on healthy remedies instead of drugs, alcohol, and other disorders.
Health and wellness coaches recommend at least 30 minutes of exercise 3 to 5 times per week regarding a regular exercise regimen. Experts stress that this doesn’t need to be a bodybuilding or cardiovascular workout in a gym; it can be gardening activities, walking around the block, going to the beach, bike riding, playing social sports et cetera.
Photo by Inzmam Khan
Photo by Pixabay